clarify description and configurations. Closing issue #28
This commit is contained in:
@@ -1,4 +1,9 @@
|
|||||||
# This adaptive Dockerfile is generated by 'generate-Dockerfile.sh' from parts within src/
|
# This Dockerfile is generated by 'generate-Dockerfile.sh' from elements within 'src/'
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# **Please do not change this file directly!**
|
||||||
|
# To adapt this Dockerfile, adapt 'generate-Dockerfile.sh' or 'src/Dockerfile.usefulpackages'.
|
||||||
|
# More information can be found in the documentation.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Use NVIDIA CUDA as base image and run the same installation as in the other packages.
|
# Use NVIDIA CUDA as base image and run the same installation as in the other packages.
|
||||||
# The version of cudatoolkit must match those of the base image, see Dockerfile.pytorch
|
# The version of cudatoolkit must match those of the base image, see Dockerfile.pytorch
|
||||||
@@ -412,12 +417,6 @@ LABEL authors="Christoph Schranz <christoph.schranz@salzburgresearch.at>, Mathem
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
USER root
|
USER root
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Install elasticsearch libs
|
|
||||||
USER root
|
|
||||||
RUN apt-get update \
|
|
||||||
&& curl -sL https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/org/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-hadoop/6.8.1/elasticsearch-hadoop-6.8.1.jar
|
|
||||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir elasticsearch==7.1.0
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir ipyleaflet plotly==4.8.* "ipywidgets>=7.5"
|
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir ipyleaflet plotly==4.8.* "ipywidgets>=7.5"
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Install important packages and Graphviz
|
# Install important packages and Graphviz
|
||||||
|
|||||||
230
README.md
230
README.md
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
|||||||
# GPU-Jupyter
|
# GPU-Jupyter
|
||||||
#### Leverage Jupyter Notebooks with the power of your NVIDIA GPU and perform GPU calculations using Tensorflow and Pytorch in collaborative notebooks.
|
#### Leverage Jupyter Notebooks with the power of your NVIDIA GPU and perform GPU calculations using Tensorflow and Pytorch in collaborative notebooks.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||

|
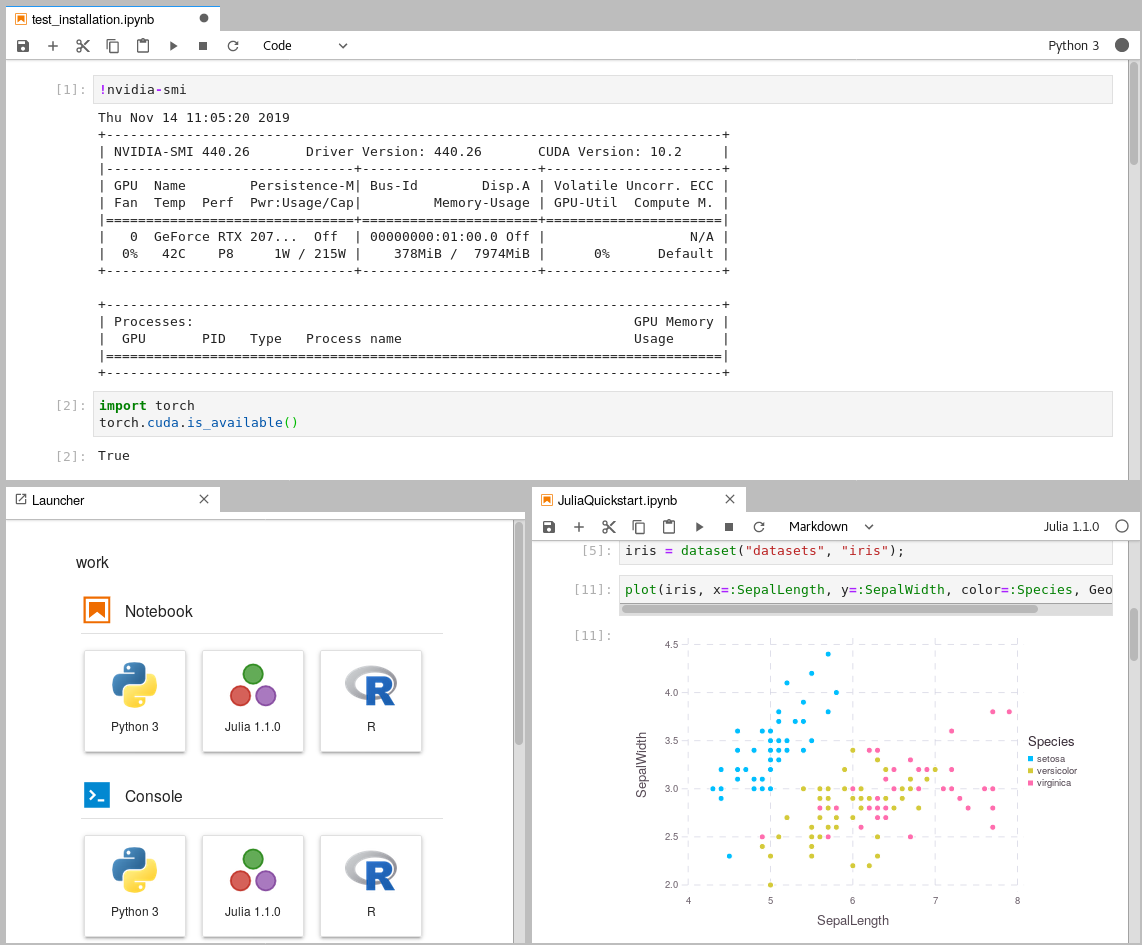
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
First of all, thanks to [docker-stacks](https://github.com/jupyter/docker-stacks)
|
First of all, thanks to [docker-stacks](https://github.com/jupyter/docker-stacks)
|
||||||
for creating and maintaining a robost Python, R and Julia toolstack for Data Analytics/Science
|
for creating and maintaining a robost Python, R and Julia toolstack for Data Analytics/Science
|
||||||
@@ -14,8 +14,8 @@ The image of this repository is available on [Dockerhub](https://hub.docker.com/
|
|||||||
1. [Requirements](#requirements)
|
1. [Requirements](#requirements)
|
||||||
2. [Quickstart](#quickstart)
|
2. [Quickstart](#quickstart)
|
||||||
3. [Tracing](#tracing)
|
3. [Tracing](#tracing)
|
||||||
4. [Deployment](#deployment-in-the-docker-swarm)
|
4. [Configuration](#configuration)
|
||||||
5. [Configuration](#configuration)
|
5. [Deployment](#deployment-in-the-docker-swarm)
|
||||||
6. [Issues and Contributing](#issues-and-contributing)
|
6. [Issues and Contributing](#issues-and-contributing)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -58,58 +58,41 @@ The image of this repository is available on [Dockerhub](https://hub.docker.com/
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
## Quickstart
|
## Quickstart
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
First of all, it is necessary to generate the `Dockerfile` based on the NIVIDA base image and the
|
First of all, it is necessary to generate the `Dockerfile` that is based on
|
||||||
[docker-stacks](https://github.com/jupyter/docker-stacks).
|
the NIVIDA base image and the [docker-stacks](https://github.com/jupyter/docker-stacks).
|
||||||
As soon as you have access to your GPU within Docker containers
|
As soon as you have access to your GPU within Docker containers
|
||||||
(make sure the command `docker run --gpus all nvidia/cuda:10.1-base-ubuntu18.04 nvidia-smi` shows your
|
(make sure the command `docker run --gpus all nvidia/cuda:10.1-base-ubuntu18.04 nvidia-smi`
|
||||||
GPU statistics), you can generate a Dockerfile, build and run it.
|
shows your GPU statistics), you can generate the Dockerfile, build and run it.
|
||||||
The following commands will start *GPU-Jupyter* on [localhost:8848](http://localhost:8848) with the default
|
The following commands will start *GPU-Jupyter* on [localhost:8848](http://localhost:8848)
|
||||||
password `asdf`.
|
with the default password `asdf`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
./generate-Dockerfile.sh
|
# generate a Dockerfile with python and without Julia and R
|
||||||
|
./generate-Dockerfile.sh --no-datascience-notebook
|
||||||
docker build -t gpu-jupyter .build/ # will take a while
|
docker build -t gpu-jupyter .build/ # will take a while
|
||||||
docker run -d -p [port]:8888 gpu-jupyter # starts gpu-jupyter WITHOUT GPU support
|
docker run -d -p [port]:8888 gpu-jupyter # starts gpu-jupyter WITHOUT GPU support
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
To run the container with GPU support, a local data volume and , run:
|
To run the container WITH GPU support, a local data volume and some other configurations, run:
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
docker run -d -it -p 8848:8888 -v $(pwd)/data:/home/jovyan/work -e GRANT_SUDO=yes -e JUPYTER_ENABLE_LAB=yes --user root --restart always --name gpu-jupyter_1 gpu-jupyter
|
docker run --gpus all -d -it -p 8848:8888 -v $(pwd)/data:/home/jovyan/work -e GRANT_SUDO=yes -e JUPYTER_ENABLE_LAB=yes --user root --restart always --name gpu-jupyter_1 gpu-jupyter
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Start via Docker Compose
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Parameter
|
The script `start-local.sh` is a wrapper for a quick configuration of the
|
||||||
|
underlying `docker-compose.yml`:
|
||||||
The script `generate-Dockerfile.sh` has multiple parameters:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
* `-c|--commit`: specify a commit or `"latest"` for the `docker-stacks`, the default commit is a working one.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
* `-s|--slim`: Generate a slim Dockerfile.
|
|
||||||
As some installations are not needed by everyone, there is the possibility to skip some installations
|
|
||||||
to reduce the size of the image.
|
|
||||||
Here the `docker-stack` `scipy-notebook` is used instead of `datascience-notebook` that comes with Julia and R.
|
|
||||||
Moreover, none of the packages within `src/Dockerfile.usefulpackages` is installed.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
* `--no-datascience-notebook`: As the name suggests, the `docker-stack` `datascience-notebook` is not installed
|
|
||||||
on top of the `scipy-notebook`, but the packages within `src/Dockerfile.usefulpackages` are.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
* `--no-useful-packages`: On top of the `docker-stack` `datascience-notebook`, the essential `gpulibs` are installed
|
|
||||||
but not the packages within `src/Dockerfile.usefulpackages`.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The script `start-local.sh` is a wrapper for a quick configuration of the underlying `docker-compose.yml`.
|
|
||||||
It is equal to these commands:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
docker build -t gpu-jupyter .build/
|
./start-local.sh -p 8848 # the default port is 8888
|
||||||
docker run -d -p [port]:8888 gpu-jupyter
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Tracing
|
## Tracing
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
With these commands we can see if everything worked well:
|
With these commands we can see if everything worked well:
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
bash show-local.sh # a env-var safe wrapper for a 'docker-compose logs -f'
|
bash show-local.sh # a env-var safe wrapper for 'docker-compose logs -f'
|
||||||
docker ps
|
docker ps
|
||||||
docker logs [service-name]
|
docker logs [service-name]
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
@@ -120,8 +103,107 @@ In order to stop the local deployment, run:
|
|||||||
./stop-local.sh
|
./stop-local.sh
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Configuration
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Configuration of the Dockerfile-Generation
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The script `generate-Dockerfile.sh` generates a Dockerfile within the `.build/`
|
||||||
|
directory.
|
||||||
|
This implies that this Dockerfile is overwritten by each generation.
|
||||||
|
The Dockerfile-generation script `generate-Dockerfile.sh`
|
||||||
|
has the following parameters (note that 2, 3 and 4 are exclusive):
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `-c|--commit`: specify a commit or `"latest"` for the `docker-stacks`,
|
||||||
|
the default commit is a working one.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `-s|--slim`: Generate a slim Dockerfile.
|
||||||
|
As some installations are not needed by everyone, there is the possibility to skip some
|
||||||
|
installations to reduce the size of the image.
|
||||||
|
Here the `docker-stack` `scipy-notebook` is used instead of `datascience-notebook`
|
||||||
|
that comes with Julia and R.
|
||||||
|
Moreover, none of the packages within `src/Dockerfile.usefulpackages` is installed.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `--no-datascience-notebook`: As the name suggests, the `docker-stack` `datascience-notebook`
|
||||||
|
is not installed
|
||||||
|
on top of the `scipy-notebook`, but the packages within `src/Dockerfile.usefulpackages` are.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
* `--no-useful-packages`: On top of the `docker-stack` `datascience-notebook` (Julia and R),
|
||||||
|
the essential `gpulibs` are installed, but not the packages within `src/Dockerfile.usefulpackages`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Custom Installations
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
**As `.build/Dockerfile` is overwritten, it is suggested to append custom installations either
|
||||||
|
within `src/Dockerfile.usefulpackages` or in `generate-Dockerfile.sh`.**
|
||||||
|
If you think some package is missing in the default stack, please let us know!
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Set the Password
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Please set a new password using `src/jupyter_notebook_config.json`.
|
||||||
|
Therefore, hash your password in the form (password)(salt) using a sha1 hash generator, e.g., the sha1 generator of [sha1-online.com](http://www.sha1-online.com/).
|
||||||
|
The input with the default password `asdf` is appended by a arbitrary salt `e49e73b0eb0e` to `asdfe49e73b0eb0e` and should yield the hash string as shown in the config below.
|
||||||
|
**Never give away your own unhashed password!**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Then update the config file as shown below and restart the service.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```json
|
||||||
|
{
|
||||||
|
"NotebookApp": {
|
||||||
|
"password": "sha1:e49e73b0eb0e:32edae7a5fd119045e699a0bd04f90819ca90cd6"
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Updates
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Deployment in the Docker Swarm
|
#### Update CUDA to another version
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Please check version compatibilities for [CUDA and Pytorch](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/)
|
||||||
|
respectively [CUDA and Tensorflow](https://www.tensorflow.org/install/gpu) previously.
|
||||||
|
To update CUDA to another version, change in `Dockerfile.header`
|
||||||
|
the line:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
FROM nvidia/cuda:10.1-base-ubuntu18.04
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
and in the `Dockerfile.pytorch` the line:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
cudatoolkit=10.1
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Then re-generate and re-run the image, as closer described above:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
./generate-Dockerfile.sh
|
||||||
|
./start-local.sh -p 8848
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#### Update Docker-Stack
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The [docker-stacks](https://github.com/jupyter/docker-stacks) are used as a
|
||||||
|
submodule within `.build/docker-stacks`. Per default, the head of the commit is reset to a commit on which `gpu-jupyter` runs stable.
|
||||||
|
To update the generated Dockerfile to a specific commit, run:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
./generate-Dockerfile.sh --commit c1c32938438151c7e2a22b5aa338caba2ec01da2
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
To update the generated Dockerfile to the latest commit, run:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bash
|
||||||
|
./generate-Dockerfile.sh --commit latest
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
A new build can last some time and may consume a lot of data traffic. Note, that the latest version may result in
|
||||||
|
a version conflict!
|
||||||
|
More info to submodules can be found in
|
||||||
|
[this tutorial](https://www.vogella.com/tutorials/GitSubmodules/article.html).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Deployment in the Docker Swarm
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
A Jupyter instance often requires data from other services.
|
A Jupyter instance often requires data from other services.
|
||||||
If that data-source is containerized in Docker and sharing a port for communication shouldn't be allowed, e.g., for security reasons,
|
If that data-source is containerized in Docker and sharing a port for communication shouldn't be allowed, e.g., for security reasons,
|
||||||
@@ -184,10 +266,14 @@ Finally, *GPU-Jupyter* can be deployed in the Docker Swarm with the shared netwo
|
|||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
where:
|
where:
|
||||||
* **-p:** port specifies the port on which the service will be available.
|
* **-p:** port specifies the port on which the service will be available.
|
||||||
* **-n:** docker-network is the name of the attachable network from the previous step, e.g., here it is **elk_datastack**.
|
* **-n:** docker-network is the name of the attachable network from the previous step,
|
||||||
* **-r:** registry port is the port that is published by the registry service, see [Set up Docker Swarm and Registry](set-up-docker-swarm-and-registry).
|
e.g., here it is **elk_datastack**.
|
||||||
|
* **-r:** registry port is the port that is published by the registry service, default is `5000`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Now, *gpu-jupyter* will be accessable here on [localhost:8848](http://localhost:8848) with the default password `asdf` and shares the network with the other data-source, i.e., all ports of the data-source will be accessable within *GPU-Jupyter*, even if they aren't routed it the source's `docker-compose` file.
|
Now, *gpu-jupyter* will be accessible here on [localhost:8848](http://localhost:8848)
|
||||||
|
with the default password `asdf` and shares the network with the other data-source, i.e.,
|
||||||
|
all ports of the data-source will be accessible within *GPU-Jupyter*,
|
||||||
|
even if they aren't routed it the source's `docker-compose` file.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Check if everything works well using:
|
Check if everything works well using:
|
||||||
```bash
|
```bash
|
||||||
@@ -200,70 +286,12 @@ In order to remove the service from the swarm, use:
|
|||||||
./remove-from-swarm.sh
|
./remove-from-swarm.sh
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Configuration
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Please set a new password using `src/jupyter_notebook_config.json`.
|
|
||||||
Therefore, hash your password in the form (password)(salt) using a sha1 hash generator, e.g., the sha1 generator of [sha1-online.com](http://www.sha1-online.com/).
|
|
||||||
The input with the default password `asdf` is appended by a arbitrary salt `e49e73b0eb0e` to `asdfe49e73b0eb0e` and should yield the hash string as shown in the config below.
|
|
||||||
**Never give away your own unhashed password!**
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Then update the config file as shown below and restart the service.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```json
|
|
||||||
{
|
|
||||||
"NotebookApp": {
|
|
||||||
"password": "sha1:e49e73b0eb0e:32edae7a5fd119045e699a0bd04f90819ca90cd6"
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Updates
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### Update CUDA to another version
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Please check version compatibilities for [CUDA and Pytorch](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/)
|
|
||||||
respectively [CUDA and Tensorflow](https://www.tensorflow.org/install/gpu) previously.
|
|
||||||
To update CUDA to another version, change in `Dockerfile.header`
|
|
||||||
the line:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
FROM nvidia/cuda:10.1-base-ubuntu18.04
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
and in the `Dockerfile.pytorch` the line:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
cudatoolkit=10.1
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Then re-generate and re-run the image, as closer described above:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```bash
|
|
||||||
./generate-Dockerfile.sh
|
|
||||||
./start-local.sh -p 8848
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### Update Docker-Stack
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The [docker-stacks](https://github.com/jupyter/docker-stacks) are used as a
|
|
||||||
submodule within `.build/docker-stacks`. Per default, the head of the commit is reset to a commit on which `gpu-jupyter` runs stable.
|
|
||||||
To update the generated Dockerfile to a specific commit, run:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```bash
|
|
||||||
./generate-Dockerfile.sh --commit c1c32938438151c7e2a22b5aa338caba2ec01da2
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
To update the generated Dockerfile to the latest commit, run:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```bash
|
|
||||||
./generate-Dockerfile.sh --commit latest
|
|
||||||
```
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
A new build can last some time and may consume a lot of data traffic. Note, that the latest version may result in
|
|
||||||
a version conflict!
|
|
||||||
More info to submodules can be found in
|
|
||||||
[this tutorial](https://www.vogella.com/tutorials/GitSubmodules/article.html).
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Issues and Contributing
|
## Issues and Contributing
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
This project has the intention to create a robust image for CUDA-based GPU-applications, which is built on top of the [docker-stacks](https://github.com/jupyter/docker-stacks). You are free to help to improve this project, by:
|
This project has the intention to create a robust image for CUDA-based GPU-applications,
|
||||||
|
which is built on top of the [docker-stacks](https://github.com/jupyter/docker-stacks).
|
||||||
|
You are free to help to improve this project, by:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
* [filing a new issue](https://github.com/iot-salzburg/gpu-jupyter/issues/new)
|
* [filing a new issue](https://github.com/iot-salzburg/gpu-jupyter/issues/new)
|
||||||
* [open a pull request](https://help.github.com/articles/using-pull-requests/)
|
* [open a pull request](https://help.github.com/articles/using-pull-requests/)
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -40,7 +40,12 @@ else
|
|||||||
fi
|
fi
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Write the contents into the DOCKERFILE and start with the header
|
# Write the contents into the DOCKERFILE and start with the header
|
||||||
echo "# This adaptive Dockerfile is generated by 'generate-Dockerfile.sh' from parts within src/
|
echo "# This Dockerfile is generated by 'generate-Dockerfile.sh' from elements within 'src/'
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# **Please do not change this file directly!**
|
||||||
|
# To adapt this Dockerfile, adapt 'generate-Dockerfile.sh' or 'src/Dockerfile.usefulpackages'.
|
||||||
|
# More information can be found in the README under configuration.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
" > $DOCKERFILE
|
" > $DOCKERFILE
|
||||||
cat src/Dockerfile.header >> $DOCKERFILE
|
cat src/Dockerfile.header >> $DOCKERFILE
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@@ -2,12 +2,6 @@ LABEL authors="Christoph Schranz <christoph.schranz@salzburgresearch.at>, Mathem
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
USER root
|
USER root
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Install elasticsearch libs
|
|
||||||
USER root
|
|
||||||
RUN apt-get update \
|
|
||||||
&& curl -sL https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/org/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-hadoop/6.8.1/elasticsearch-hadoop-6.8.1.jar
|
|
||||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir elasticsearch==7.1.0
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir ipyleaflet plotly==4.8.* "ipywidgets>=7.5"
|
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir ipyleaflet plotly==4.8.* "ipywidgets>=7.5"
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Install important packages and Graphviz
|
# Install important packages and Graphviz
|
||||||
|
|||||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user